The concept of endangered animals is not new, but its relevance and urgency have increased dramatically in recent decades. Biodiversity is crucial for the balance of ecosystems and the health of the planet. However, many animal species are on the verge of extinction due to various human activities. This article explores the causes of extinction, some of the most endangered animals and initiatives for their conservation.
Causes of Extinction.
Habitat Destruction.
Habitat destruction is one of the main causes of species extinction. Deforestation, urbanization and intensive agriculture have drastically reduced the natural spaces where animals live and reproduce. For example, the Amazon rainforest, home to countless species, has been devastated by slashing and burning to create agricultural land.
Climate change.
Climate change alters ecosystems and affects animals that cannot adapt quickly to new conditions. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and increases in extreme weather events are affecting species around the world. The polar bear, for example, depends on sea ice for hunting and with melting glaciers, its survival is seriously threatened.
Hunting and Exploitation.
Poaching and commercial exploitation are also significant factors in the decline of animal populations. The illegal trade in exotic species and animal parts, such as elephant ivory and rhino horn, continues to drive poaching. Despite international efforts to control these activities, many species continue to be hunted illegally.
Pollution.
Pollution of water, air and soil affects the health of animals and their habitats. Oil spills, plastic waste and toxic chemicals are particularly harmful. Marine species, such as turtles and fish, ingest plastics, which can be fatal. Additionally, noise pollution in the oceans interferes with the communication and navigation of cetaceans.
Endangered animals.
Bengal tiger.
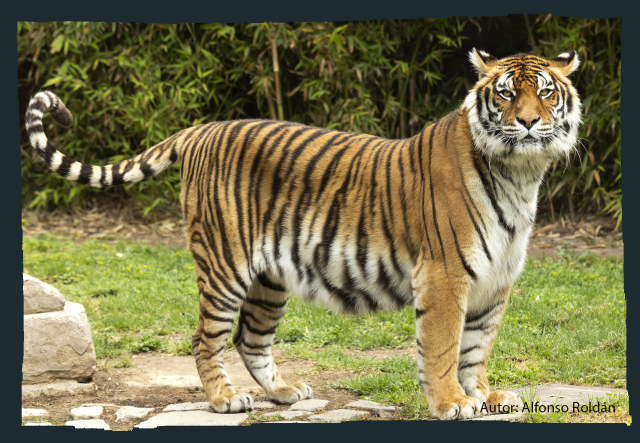

The Bengal tiger is one of the most iconic tiger subspecies and also one of the most endangered. Habitat loss and poaching for their skin and other organs have reduced their population to a few thousand in the wild. Conservation initiatives in India and Bangladesh have helped stabilize some populations, but the threat remains.
Javan rhinoceros.
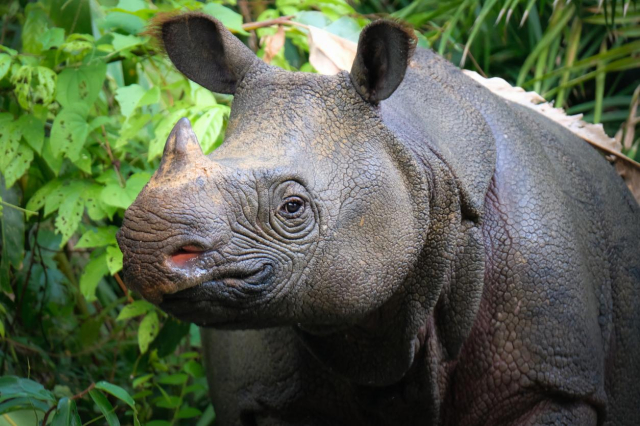

The Javan rhinoceros is one of the rarest mammals in the world, with fewer than 70 individuals known to survive in the wild, all of them in the Ujung Kulon National Park in Indonesia. Habitat loss and poaching have decimated their population. Strict protection measures and intensive surveillance have been crucial to avoid its total extinction.
Bornean orangutan.
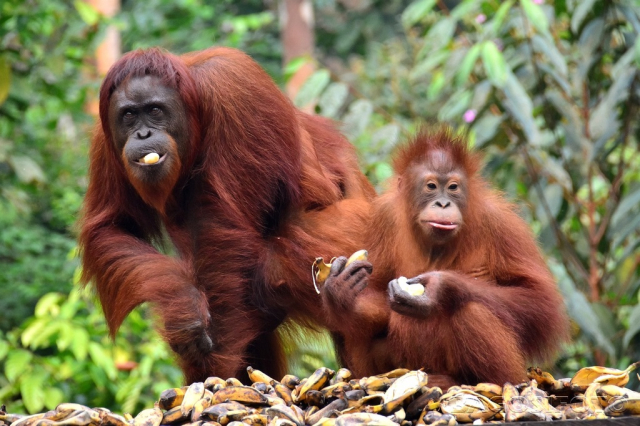

The Bornean orangutan is another example of a species in serious danger of extinction due to deforestation and the expansion of oil palm plantations. These highly intelligent and social primates have lost much of their natural habitat, and their population has declined significantly. Rehabilitation and reforestation efforts are vital to their survival.
Vaquita Marina.
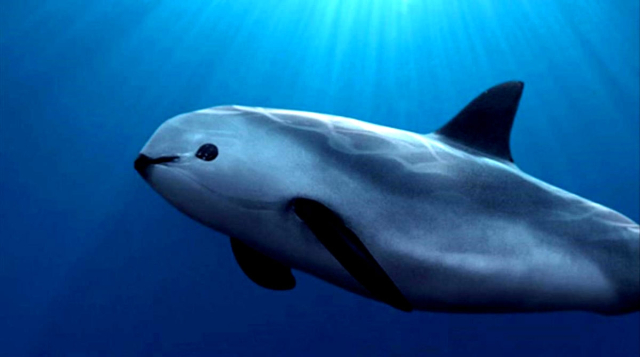
The vaquita porpoise, the smallest cetacean in the world, is critically endangered. It resides in the Gulf of California, Mexico, and its population has been devastated by bycatch in gillnets used to capture totoaba, a fish whose maw is highly coveted in traditional Chinese medicine. It is estimated that there are fewer than 30 vaquitas left in the wild, and the fight to save them is a race against time.
Hawksbill turtle.

The hawksbill turtle is another seriously endangered species. It is found in tropical and subtropical waters around the world. The commercial exploitation of its shell, used to make jewelry and other decorative objects, has been one of the main causes of its decline. In addition, habitat loss, marine pollution and egg collection also contribute to their critical situation.
Conservation Initiatives.
Natural Reserves and National Parks.
The creation of nature reserves and national parks is a key strategy for the conservation of endangered species. These protected spaces provide safe havens where animals can live and reproduce without the threat of destructive human activity. Parks such as Yellowstone National Park in the United States and Kruger National Park in South Africa are successful examples of conservation.
Captive Reproduction Programs.
Captive breeding programs play a crucial role in the conservation of critically endangered species. These programs seek to increase the population of animals in captivity with the aim of reintroducing them into their natural habitats. Notable examples include the breeding program for the California condor and the giant panda.
Legislation and International Agreements.
International laws and agreements are essential to protect endangered species. The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) regulates international trade in endangered species to prevent their exploitation. Additionally, many nations have implemented strict laws to protect wildlife and punish poaching.
Awareness and Education.
Education and public awareness are vital for long-term conservation. Educational campaigns can change human attitudes and behaviors towards wildlife and the environment. School programs, documentaries and social media campaigns have raised awareness about the importance of protecting endangered species.
Conservation Technology.
Technology also plays an increasingly important role in conservation. Drones, camera traps and GPS tracking devices allow conservationists to monitor animal populations and their movements more effectively. These tools help collect crucial data and make informed decisions for wildlife management.
Species extinction is a global problem that requires urgent attention and action. The loss of biodiversity not only affects the animals directly involved, but also ecosystems and humanity. The causes of extinction are varied, but they are all linked to human activity. Through the creation of nature reserves, captive breeding programs, strict legislation, public awareness and the use of advanced technology, it is possible to protect and conserve endangered species.
The global effort to save endangered animals must be continuous and multifaceted. Every small action counts, and collaboration between governments, non-governmental organizations, local communities and citizens around the world is essential to ensure a future where all species can thrive.
