Ecuador, a country located in the heart of South America, is known for its surprising geographical and climatic diversity. This compact nation is home to a variety of ecosystems, from dense rainforests to snow-capped peaks of the Andes. Much of this diversity is due to the climatic floors that extend throughout its territory, offering a wide range of environments and climatic conditions. In this article, we will explore in depth the different climatic zones of Ecuador and their importance in the biodiversity, culture and daily life of its inhabitants.
The climatic floors.
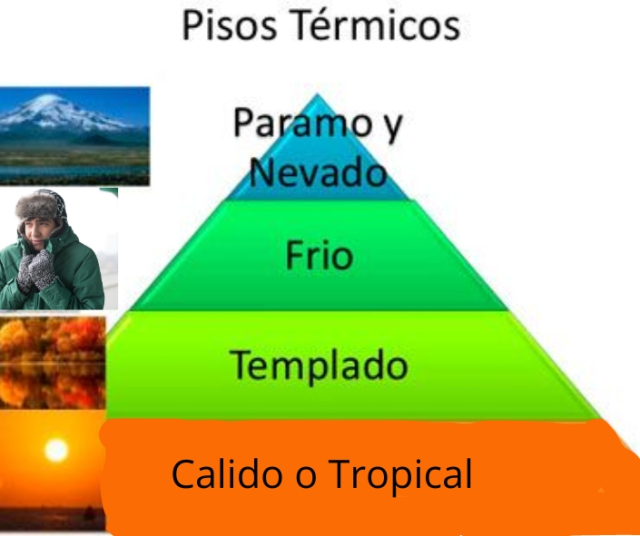
The climatic floors of Ecuador are a classification that divides the country into different zones according to variations in altitude, temperature and humidity. These floors influence the distribution of vegetation, fauna and human activities, and are fundamental to understanding the geography and climate of the country. The main climatic zones of Ecuador are: the tropical zone, the subtropical zone, the temperate zone, the cold zone and the paramo zone.
Tropical floor.
The tropical zone covers the low-altitude regions on the Pacific coast and the Amazon rainforest in the east of the country. Characterized by high temperatures and high humidity, this floor is home to lush tropical vegetation, including a wide variety of leafy trees, palms and epiphytic plants. The biodiversity in these areas is extraordinary, with an abundance of bird, mammal, reptile and amphibian species.
Subtropical floor.
The subtropical floor is found in the eastern foothills of the Andes, at moderate altitudes. Here, temperatures are cooler than in tropical regions, but still warm year-round. The vegetation is diverse, with a mix of tropical and subtropical species, including cloud and mist forests. This region is known for its impressive biodiversity and is home to a variety of endemic species.
Tempered floor.
The temperate floor is found in the highlands of the Sierra, at altitudes ranging from 1500 to 3000 meters above sea level. Here, temperatures are cooler and the seasons are more defined. The predominant vegetation is the Andean forest, which consists of a mixture of evergreen and deciduous trees, as well as a variety of shrubs and herbaceous plants. This region is known for its fertile valleys and picturesque landscapes.
Cold floor.
The cold floor is found in the peaks of the Andes, at altitudes greater than 3000 meters above sea level. Here, temperatures are cold all year round, with frequent frosts and occasional snowfall. The predominant vegetation is high altitude grasslands and mountain scrub, adapted to the harsh climatic conditions. This region is home to a variety of cold-adapted flora and fauna species, including Andean camelids such as the llama and alpaca.
Moorland floor.
The paramo floor is found in the highest peaks of the Andes, at altitudes that exceed 4000 meters above sea level. Here, temperatures are cold and the weather is extremely variable, with strong winds and unpredictable weather conditions. The predominant vegetation is the moors, unique high mountain ecosystems characterized by dense vegetation adapted to the cold, such as the frailejón. These areas are important for water regulation and maintaining biodiversity.
Glacial floor.
The glacial floor, also known as the ice wasteland, is found at extremely high altitudes, generally above 5,000 meters above sea level. These high elevations allow low temperatures to maintain the accumulation of snow and ice throughout the year, forming permanent glaciers. These glaciers are important sources of fresh water, feeding the rivers and streams that descend from the mountains and providing water for agriculture and human consumption in nearby regions.
Importance and threats.
Despite their ecological importance and value as a water resource, Ecuador's glaciers are experiencing rapid retreat due to climate change. Rising global temperatures are causing accelerated melting of glaciers, which has significant implications for communities that depend on meltwater for their livelihoods. This retreat also affects local biodiversity and can increase the risk of natural disasters, such as floods and landslides, in surrounding areas.
Research and conservation.
Given the importance of glaciers for water supply and ecosystem conservation, research is being carried out to monitor their condition and better understand the effects of climate change. Additionally, conservation measures are being implemented to protect these fragile ecosystems, such as the creation of protected areas and the promotion of sustainable land and water use practices.
Importance of climatic floors.
Ecuador's climatic zones are of great importance for the country's biodiversity, agriculture, tourism and culture. These different climate zones are home to an incredible diversity of ecosystems and species, providing habitats for a variety of flora and fauna. In addition, climatic zones influence human activities, determining agricultural practices, traditional clothing and cultural festivities of local communities.
The climatic floors of Ecuador are an example of the amazing geographical and climatic diversity of the country. From rainforests to the snow-capped peaks of the Andes, each region has its own unique set of natural and cultural features. These climatic floors are fundamental for the country's biodiversity and environmental sustainability, and their conservation is crucial to guarantee the well-being of present and future generations.